KVM VPS vs. OpenVZ

KVM and OpenVZ are two popular virtualization technologies offered within the SolusVM environment. Understanding the distinctions between these options is crucial for making informed decisions regarding your virtualization needs.
KVM VPS: True Virtualization
KVM, or Kernel-based Virtual Machine, provides true virtualization where each virtual private server (VPS) operates independently, similar to a dedicated server. This technology enables complete isolation and allows users to run their own kernel and modify their server environment according to their requirements. KVM offers robust functionality and supports various operating systems, including Windows and BSD. It provides enhanced security and stability, making it a reliable choice for many users. Learn more about VPS KVM Hosting.
OpenVZ: Container-based Virtualization
OpenVZ, on the other hand, utilizes a container-based virtualization approach that relies on the host node’s kernel. It allows for efficient resource utilization by sharing the host’s kernel with multiple VPS containers. While OpenVZ offers high performance and low overhead within the containers, it comes with certain limitations. Users have less flexibility in terms of customization and cannot modify the kernel or use different operating systems. However, OpenVZ provides lightweight virtualization and can be a suitable choice for specific use cases where resource efficiency is prioritized. Learn more about OpenVZ Hosting.
Key Differences
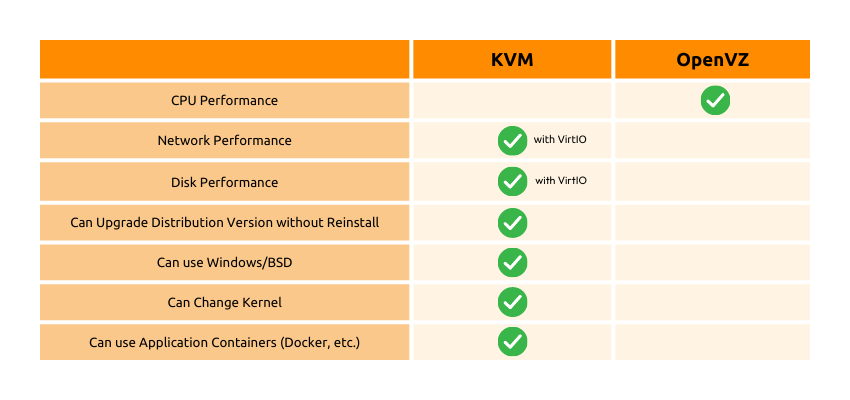
Let’s explore the key differences between KVM and OpenVZ:
- Isolation
KVM provides complete isolation as each VPS operates independently with its own kernel, whereas OpenVZ shares the host node’s kernel among containers. - Operating Systems
KVM supports a wide range of operating systems, including Windows and BSD, while OpenVZ is limited to Linux-based distributions. - Customization
KVM allows users to modify the server environment, change the kernel, and upgrade distribution versions without reinstalling, offering greater customization options. OpenVZ has limitations in terms of kernel modifications and operating system choices. - Resource Allocation
KVM allocates dedicated resources to each VPS, including CPU, network, and disk resources. OpenVZ shares resources among containers, which can result in more efficient resource utilization. - Stability
KVM is known for its stability and reliability due to the independent operation of each VPS. OpenVZ can be susceptible to stability issues if the host node experiences any problems.
It’s important to carefully consider your specific requirements and preferences when choosing between KVM and OpenVZ. The decision should be based on factors such as the level of isolation, customization needs, supported operating systems, and resource allocation.
Want to learn more about KVM or OpenVZ solutions?
To learn more about our KVM and OpenVZ products and find the perfect virtualization solution for your needs, visit our homepage or contact our support team. By understanding the differences between KVM and OpenVZ, you can make an informed choice and select the virtualization technology that best suits your needs.
